Irregular moon
In astronomy, an irregular moon is a natural satellite following a distant, inclined, and often eccentric and retrograde orbit. They are believed to have been captured by their parent planet, unlike regular satellites, which form in situ.
Ninety-three irregular satellites have been discovered since 1997, orbiting all four of the giant planets (Jupiter, Saturn, Uranus and Neptune). Before 1997, only ten were known, including Phoebe, the largest irregular satellite of Saturn, and Himalia, the largest irregular satellite of Jupiter. Sycorax, the largest irregular moon of Uranus, was discovered in 1997. It is currently thought that the irregular satellites were captured from heliocentric orbits near their current locations, shortly after the formation of their parent planet. An alternative theory, that they originated further out in the Kuiper belt, is not supported by current observations.
Contents |
Definition
| Planet | rH (Gm)[1] |
|---|---|
| Jupiter | 51 |
| Saturn | 69 |
| Uranus | 73 |
| Neptune | 116 |
There is no widely accepted precise definition of an irregular satellite. Informally, satellites are considered irregular if they are far enough from the planet that the precession of their orbital plane is primarily controlled by the Sun.
In practice, the satellite's semi-major axis is compared with the planet's Hill sphere (that is, the sphere of its gravitational influence) 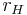 . Irregular satellites have semi-major axes greater than 0.05
. Irregular satellites have semi-major axes greater than 0.05 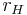 with apoapses extending as far as to 0.65
with apoapses extending as far as to 0.65 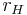 .[1] The radius of the Hill sphere is given in the adjacent table.
.[1] The radius of the Hill sphere is given in the adjacent table.
Orbits
Current distribution
The orbits of the known irregular satellites are extremely diverse, but there are certain rules. Retrograde orbits are far more common (83%) than prograde orbits. No satellites are known with orbital inclinations higher than 55° (or smaller than 130° for retrograde satellites). In addition, some groupings can be identified, in which one large satellite shares a similar orbit with a few smaller ones.
Given their distance from the planet, the orbits of the outer satellites are highly perturbed by the Sun and their orbital elements change widely over short intervals. The semi-major axis of Pasiphae, for example, changes as much as 1.5 Gm in two years (single orbit), the inclination around 10°, and the eccentricity as much as 0.4 in 24 years (twice Jupiter’s orbit period).[2] Consequently, mean orbital elements (averaged over time) are used to identify the groupings rather than osculating elements at the given date. (Similarly, the proper orbital elements are used to determine the families of asteroids.)
Origin
Irregular satellites are believed to have been captured from heliocentric orbits. (Indeed, it appears that the irregular moons of the gas giants, the Jovian and Neptunian trojans, and grey Kuiper belt objects have a similar origin.[3]) For this to occur, one of three things needs to have happened:
- energy dissipation (e.g. in interaction with the primordial gas cloud)
- a substantial (40%) extension of the planet's Hill sphere in a brief period of time (thousands of years)
- a transfer of energy in a three-body interaction. This could involve:
- a collision (or close encounter) of an incoming body and a satellite, resulting in the incoming body losing energy and being captured.
- a close encounter between an incoming binary object and the planet (or possibly an existing moon), resulting in one component of the binary being captured. Such a route has been suggested as most likely for Triton.[4]
After the capture, some of the satellites could break up leading to groupings of smaller moons following similar orbits. Resonances could further modify the orbits making these groupings less recognizable.
Long-term stability
Remarkably, the current orbits prove stable in numerical simulations, in spite of substantial perturbations near the apocenter.[5] The cause of this stability in a number of irregulars is the fact that they orbit with a secular or Kozai resonance.[6]
In addition, simulations indicate the following conclusions:
- Orbits with inclinations higher than 50° (or 130° for retrograde orbits) are very unstable: their eccentricity increases quickly resulting in the satellite being lost[2]
- Retrograde orbits are more stable than prograde (stable retrograde orbits can be found further from the planet)
Increasing eccentricity results in smaller pericenters and large apocenters. The satellites enter the zone of the regular (larger) moons and are lost or ejected via collision and close encounters. Alternatively, the increasing perturbations by the Sun at the growing apocenters push them beyond the Hill sphere.
Retrograde satellites can be found further from the planet than prograde ones. Detailed numerical integrations have shown this asymmetry. The limits are a complicated function of the inclination and eccentricity, but in general, prograde orbits with semi-major axes up to 0.47 rH (Hill sphere radius) can be stable, while for retrograde orbits stability can extend out to 0.67 rH.
The boundary for the semimajor axis is surprisingly sharp for the prograde satellites. A satellite on a prograde, circular orbit (inclination=0°) placed at 0.5 rH would leave Jupiter in as little as forty years. The effect can be explained by so called evection resonance. The apocenter of the satellite, where the planet’s grip on the moon is at its weakest, gets locked in resonance with the position of the Sun. The effects of the perturbation accumulate at each passage pushing the satellite even further outwards.[5]
The asymmetry between the prograde and retrograde satellites can be explained very intuitively by the Coriolis acceleration in the frame rotating with the planet. For the prograde satellites the acceleration points outward and for the retrograde it points inward, stabilising the satellite.[7]
Physical characteristics
Size
Given their greater distance from Earth, the known irregular satellites of Uranus and Neptune are larger than those of Jupiter and Saturn; smaller ones probably exist but have not yet been observed. However, with this observational bias in mind, the size distribution is similar for all four giant planets.
Typically, the relation expressing the number  of objects of the diameter smaller or equal to
of objects of the diameter smaller or equal to 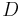 is approximated by a power law:
is approximated by a power law:
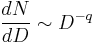 with q defining the slope.
with q defining the slope.
A shallow power law (q~2) is observed for sizes 10 to 100 km† but steeper (q~3.5) for objects smaller than 10 km‡ .
For comparison, the distribution of Kuiper Belt objects is much steeper (q~4), i.e. for one object of 1000 km there are a thousand objects with a diameter of 100 km. The size distribution provides insights into the possible origin (capture, collision/break-up or accretion).
†For every object of 100 km, ten objects of 10 km can be found.
‡For one object of 10 km, some 140 objects of 1 km can be found.
Colours
The colours of irregular satellites can be studied via colour indices: simple measures of differences of the apparent magnitude of an object through blue (B), visible i.e. green-yellow (V), and red (R) filters. The observed colours of the irregular satellites vary from neutral (greyish) to reddish (but not as red as the colours of some Kuiper Belt objects).
| albedo[8] | neutral | reddish | red |
|---|---|---|---|
| low | C 3-8% | P 2-6% | D 2-5% |
| medium | M 10-18% | A 13-35% | |
| high | E 25-60% |
Each planet's system displays slightly different characteristics. Jupiter's irregulars are grey to slightly red, consistent with C, P and D-type asteroids.[9] Some groups of satellites are observed to display similar colours (see later sections). Saturn's irregulars are slightly redder than those of Jupiter. The large Uranian irregular satellites (Sycorax and Caliban) are found light-red while smaller Prospero and Setebos are grey as are Neptunian sateliites Nereid and Halimede.[10]
Spectra
With the current resolution, the visible and near-infrared spectra of most satellites appear featureless. So far, water ice has been inferred on Phoebe and Nereid and features attributed to aqueous alteration were found on Himalia.
Rotation
Regular satellites are usually tidally locked (that is, their orbit is synchronous with their rotation so that they only show one face toward their parent planet). In contrast, tidal forces on the irregular satellites are negligible given their distance from the planet, and rotation periods in the range of only ten hours have been measured for the biggest moons Himalia, Phoebe and Nereid (to compare with their orbital periods of hundreds of days). Such rotation rates are in the same range that is typical for asteroids.
Families with a common origin
Some irregular satellites appear to orbit in 'groups', in which several satellites share similar orbits. The leading theory is that these objects constitute collisional families, parts of a larger body that broke up.
Dynamic groupings
Simple collision models can be used to estimate the possible dispersion of the orbital parameters given a velocity impulse δV. Applying these models to the known orbital parameters makes possible to estimate the δV necessary to create the observed dispersion. It is believed that δV of tens of meters per seconds (5–50 m/s) could result from a break-up. Dynamical groupings of irregular satellites can be identified using these criteria and the likelihood of the common origin from a break-up evaluated.[11]
When the dispersion of the orbits is too wide (i.e. it would require δV in the order of hundreds of m/s)
- either more than one collision must be assumed, i.e. the cluster should be further subdivided into groups
- or significant post-collision changes, for example resulting from resonances, must be postulated.
Colour groupings
When the colours and spectra of the satellites are known, the homogeneity of these data for all the members of a given grouping is a substantial argument for a common origin. However, lack of precision in the available data often makes it difficult to draw statistically significant conclusions. In addition, the observed colours are not necessarily representative of the bulk composition of the satellite.
Observed groupings
Irregular satellites of Jupiter
Typically, the following groupings are listed (dynamically tight groups displaying homogenous colours are listed in bold)
- Prograde satellites
- The Himalia group shares an average inclination of 28°. They are confined dynamically (δV ≈ 150 m/s). They are homogenous at visible wavelengths (having neutral colours similar to those of C-type asteroids) and at near infrared wavelengths[12]
- Themisto is so far believed to be isolated.
- Carpo is so far believed to be isolated.
- Retrograde satellites
- The Carme group shares an average inclination of 165°. It is dynamically tight (5 < δV < 50 m/s). It is very homogenous in colour, each member displaying light red colouring consistent with a D-type asteroid progenitor.
- The Ananke group shares an average inclination of 148°. It shows little dispersion of orbital parameters (15 < δV < 80 m/s). Ananke itself appears light red but the other group members are grey.
- The Pasiphae group is very dispersed. Pasiphae itself appears to be grey while other members (Callirrhoe, Megaclite) are light red
Sinope, sometimes included into Pasiphae group, is red and given the difference in inclination, it could be captured independently.[9][13] Pasiphae and Sinope are also trapped in a secular resonances with Jupiter.[5][11]
Irregular satellites of Saturn
The following groupings are commonly listed for Saturn's satellites:
- Prograde satellites
- The Gallic group shares an average inclination of 34°. Their orbits are dynamically tight (δV ≈ 50 m/s), and they are light red in colour; the colouring is homogenous at both visible and near infra-red wavelengths.[12]
- The Inuit group shares an average inclination of 46°. Their orbits are widely dispersed (δV ≈ 350 m/s) but they are physically homogenous, sharing a light red colouring.
- Retrograde satellites
- The Norse group is defined mostly for naming purposes; the orbital parameters are very widely dispersed. Sub-divisions have been investigated, including
Irregulars of Uranus and Neptune
| Planet | rmin[1] |
|---|---|
| Jupiter | 1.5 km |
| Saturn | 3 km |
| Uranus | 7 km |
| Neptune | 16 km |
According to current knowledge, the number of irregular satellites orbiting Uranus and Neptune is smaller than that of Jupiter and Saturn. However, it is believed this is simply a result of observational difficulties due to the greater distance of Uranus and Neptune. The table at left shows the minimum radius (rmin) of satellites that can be detected with current technology, assuming an albedo of 0.04; thus, there are almost certainly small Uranian and Neptunian moons that cannot yet be seen.
Due to the smaller numbers, statistically significant conclusions about the groupings are difficult. A single origin for the retrograde irregulars of Uranus seems unlikely given a dispersion of the orbital parameters that would require high impulse (δV ≈ 300 km) implying a large diameter of the impactor (395 km), which is incompatible in turn with the size distribution of the fragments. Instead, the existence of two groupings has been speculated[9]:
These two groups are distinct (with 3σ confidence) in their distance from Uranus and in their eccentricity.[14] However, these groupings are not directly supported by the observed colours: Caliban and Sycorax appear light red while the smaller moons are grey.[10]
For Neptune, a possible common origin of Psamathe and Neso has been noted.[15] Given the similar (grey) colours, it was also suggested that Halimede could be a fragment of Nereid.[10] The two satellites have had a very high probability (41%) of collision over the age of the solar system.[16]
Exploration
To date, the only irregular satellite to have been visited by a spacecraft is Phoebe, the largest of Saturn's irregulars, which was photographed by the Cassini probe in 2005. Cassini also captured a distant, low resolution image of Jupiter's Himalia in 2000. There are no spacecraft planned to visit any irregular satellites in the future.
References
- ^ a b c Scott S. Sheppard, Outer irregular satellites of the planets and their relationship with asteroids, comets and Kuiper Belt objects Asteroids, Comets, Meteors, Proceedings of the 229th Symposium of the International Astronomical Union held in Rio de Janeiro, Brasil August 7–12, 2005, Cambridge University Press, 2006., pp. 319-334 (preprint)
- ^ a b Carruba, V.; Burns, J. A.; Nicholson, P. D.; Gladman, B. J.; On the Inclination Distribution of the Jovian Irregular Satellites, Icarus, 158 (2002), pp. 434–449 (pdf)
- ^ Sheppard, S. S.; Trujillo, C. A. (2006). "A Thick Cloud of Neptune Trojans and Their Colors" (PDF). Science 313 (5786): 511–514. Bibcode 2006Sci...313..511S. doi:10.1126/science.1127173. PMID 16778021. http://www.ciw.edu/users/sheppard/pub/Sheppard06NepTroj.pdf.
- ^ Agnor, C. B. and Hamilton, D. P. (2006). "Neptune's capture of its moon Triton in a binary-planet gravitational encounter". Nature 441 (7090): 192–4. Bibcode 2006Natur.441..192A. doi:10.1038/nature04792. PMID 16688170.
- ^ a b c Nesvorný, D.; Alvarellos, J. L. A.; Dones, L.; and Levison, H. F.; Orbital and Collisional Evolution of the Irregular Satellites, The Astronomical Journal,126 (2003), pp. 398–429. [1]
- ^ Ćuk, M. and Burns, J. A.; A New Model for the Secular Behavior of the Irregular Satellites, American Astronomical Society, DDA meeting #35, #09.03; Bulletin of the American Astronomical Society, Vol. 36, p. 864 (preprint)
- ^ Hamilton, D. P.; and Burns, J. A.; Orbital Stability Zones about Asteroids, Icarus 92 (1991), pp. 118-131D.
- ^ Based on the definitions from Oxford Dictionary of Astronomy, ISBN 0-19-211596-0
- ^ a b c Grav, T.; Holman, M. J.; Gladman, B. J.; and Aksnes, K.; Photometric survey of the irregular satellites, Icarus, 166 (2003), pp. 33-45 (preprint).
- ^ a b c Grav, Tommy; Holman, Matthew J.; Fraser, Wesley C. (2004-09-20). "Photometry of Irregular Satellites of Uranus and Neptune". The Astrophysical Journal 613 (1): L77–L80. arXiv:astro-ph/0405605. Bibcode 2004ApJ...613L..77G. doi:10.1086/424997.
- ^ a b Nesvorný, D.; Beaugé, C.; and Dones, L.; Collisional Origin of Families of Irregular Satellites, The Astronomical Journal, 127 (2004), pp. 1768–1783 (pdf)
- ^ a b Grav, T.; and Holman, M. J.; Near-Infrared Photometry of the Irregular Satellites of Jupiter and Saturn,The Astrophysical Journal, 605, (2004), pp. L141–L144 (preprint).
- ^ Sheppard, S. S.; and Jewitt, D. C.; An abundant population of small irregular satellites around Jupiter, Nature, 423 (May 2003), pp. 261-263 (pdf)
- ^ Sheppard, S. S.; Jewitt, D. C.; and Kleyna, J.; An Ultradeep Survey for Irregular Satellites of Uranus: Limits to Completeness, The Astronomical Journal, 129 (2005), pages 518–525 (preprint).
- ^ Sheppard, Scott S.; Jewitt, David C.; Kleyna, Jan (2006). "A Survey for "Normal" Irregular Satellites around Neptune: Limits to Completeness". The Astronomical Journal 132: 171–176. arXiv:astro-ph/0604552. Bibcode 2006AJ....132..171S. doi:10.1086/504799.
- ^ Holman, M. J.; Kavelaars, J. J.; Grav, T. et al. (2004). "Discovery of five irregular moons of Neptune" (PDF). Nature 430 (7002): 865–867. Bibcode 2004Natur.430..865H. doi:10.1038/nature02832. PMID 15318214. https://www.cfa.harvard.edu/~mholman/nature_final.pdf. Retrieved 2011-10-24.
External links
- David Jewitt's pages
- Scott Sheppard's pages
- Discovery circumstances from JPL
- Mean orbital elements from JPL
- MPC: Natural Satellites Ephemeris Service
|
|||||||||||||||||